Table of Contents
1. Introduction to C++
1.1 Programming (general)
1.2 Programming basics
1.3 Comments and whitespace
1.4 Errors and warnings
1.5 Computers and programs (general)
1.6 Computer tour
1.7 Language history
1.8 Problem solving
1.9 Why programming
1.10 Why whitespace matters
1.11 C++ example: Salary Calculation
1.12 C++ example: Married-couple names
2. Variables / Assignments
2.1 Variables and assignments (general)
2.2 Variables (int)
2.3 Identifiers
2.4 Arithmetic expressions (general)
2.5 Arithmetic expressions (int)
2.6 Example: Health data
2.7 Floating-point numbers (double)
2.8 Scientific notation for floating-point literals
2.9 Constant variables
2.10 Using math functions
2.11 Integer division and modulo
2.12 Type conversions
2.13 Binary
2.14 Characters
2.15 Strings
2.16 Integer overflow
2.17 Numeric data types
2.18 Unsigned
2.19 Random numbers
2.20 Debugging
2.21 Auto (since C++11)
2.22 Style guidelines
2.23 C++ example: Salary calculation with variables
2.24 C++ example: Married-couple names with variables
3. Branches
3.1 If-else branches (general)
3.2 If-else
3.3 More if-else
3.4 Equality and relational operators
3.5 Detecting ranges (general)
3.6 Detecting ranges with if-else statements
3.7 Logical operators
3.8 Order of evaluation
3.9 Example: Toll calculation
3.10 Switch statements
3.11 Boolean data type
3.12 String comparisons
3.13 String access operations
3.14 Character operations
3.15 More string operations
3.16 Conditional expressions
3.17 Floating-point comparison
3.18 Short circuit evaluation
3.19 C++ example: Salary calculation with branches
3.20 C++ example: Search for name using branches
4. Loops
4.1 Loops (general)
4.2 While loops
4.3 More while examples
4.4 For loops
4.5 More for loop examples
4.6 Loops and strings
4.7 Nested loops
4.8 Developing programs incrementally
4.9 Break and continue
4.10 Variable name scope
4.11 Enumerations
4.12 C++ example: Salary calculation with loops
4.13 C++ example: Domain name validation with loops
5. Arrays / Vectors
5.1 Array concept (general)
5.2 Vectors
5.3 Array iteration drill
5.4 Iterating through vectors
5.5 Multiple vectors
5.6 Vector resize
5.7 Vector push_back
5.8 Loop-modifying or copying/comparing vectors
5.9 Swapping two variables (General)
5.10 Debugging example: Reversing a vector
5.11 Arrays vs. vectors
5.12 Two-dimensional arrays
5.13 Char arrays / C strings
5.14 String library functions
5.15 Char library functions: ctype
5.16 C++ example: Annual salary tax rate calculation with vectors
5.17 C++ example: Domain name validation with vectors
6. User-Defined Functions
6.1 User-defined function basics
6.2 Return
6.3 Reasons for defining functions
6.4 Functions with branches/loops
6.5 Unit testing (functions)
6.6 How functions work
6.7 Functions: Common errors
6.8 Pass by reference
6.9 Functions with string/vector parameters
6.10 Functions with C string parameters
6.11 Scope of variable/function definitions
6.12 Default parameter values
6.13 Function name overloading
6.14 Parameter error checking
6.15 Preprocessor and include
6.16 Separate files
6.17 C++ example: Salary calculation with functions
6.18 C++ example: Domain name validation with functions
7. Objects and Classes
7.1 Objects: Introduction
7.2 Using a class
7.3 Defining a class
7.4 Inline member functions
7.5 Mutators, accessors, and private helpers
7.6 Initialization and constructors
7.7 Classes and vectors/classes
7.8 Separate files for classes
7.9 Choosing classes to create
7.10 Unit testing (classes)
7.11 Constructor overloading
7.12 Constructor initializer lists
7.13 The ‘this’ implicit parameter
7.14 Operator overloading
7.15 Overloading comparison operators
7.16 Vector ADT
7.17 Namespaces
7.18 Static data members and functions
7.19 C++ example: Salary calculation with classes
7.20 C++ example: Domain name availability with classes
8. Pointers
8.1 Why pointers?
8.2 Pointer basics
8.3 Operators: new, delete, and ->
8.4 String functions with pointers
8.5 A first linked list
8.6 Memory regions: Heap/Stack
8.7 Destructors
8.8 Memory leaks
8.9 Copy constructors
8.10 Copy assignment operator
8.11 Rule of three
8.12 C++ example: Employee list using vectors
9. Streams
9.1 Output and input streams
9.2 Output formatting
9.3 Input string stream
9.4 Output string stream
9.5 File input
9.7 File output
9.6 C++ example: Parsing and validating input files
9.8 C++ example: Saving and retrieving program data
9.9 Overloading stream operators
10. Inheritance
10.1 Derived classes
10.2 Access by members of derived classes
10.3 Overriding member functions
10.4 Polymorphism and virtual member functions
10.5 Abstract classes: Introduction (generic)
10.6 Abstract classes
10.7 Is-a versus has-a relationships
10.8 UML
10.9 C++ example: Employees and overriding class functions
10.10 C++ example: Employees using an abstract class
11. Recursion
11.1 Recursion: Introduction
11.2 Recursive functions
11.3 Recursive algorithm: Search
11.4 Adding output statements for debugging
11.5 Creating a recursive function
11.6 Recursive math functions
11.7 Recursive exploration of all possibilities
11.8 Stack overflow
11.9 C++ example: Recursively output permutations
12. Exceptions
12.1 Exception basics
12.2 Exceptions with functions
12.3 Multiple handlers
12.4 C++ example: Generate number format exception
13. Templates
13.1 Function templates
13.2 Class templates
13.3 C++ example: Map values using a function template
14. Containers
14.1 Range-based for loop
14.2 List
14.3 Pair
14.4 Map
14.5 Set
14.6 Queue
14.7 Deque
14.8 find() function
14.9 sort() function
15. Searching and Sorting Alg.
15.1 Searching and algorithms
15.2 Binary search
15.3 O notation
15.4 Algorithm analysis
15.5 Sorting: Introduction
15.6 Selection sort
15.7 Insertion sort
15.8 Quicksort
15.9 Merge sort
16. Additional Material
16.1 Do-while loops
16.2 Arrays
16.3 Iterating through arrays
16.4 Multiple arrays
16.5 Loop-modifying or copying/comparing arrays
16.6 Debugging example: Reversing an array
16.7 Engineering examples
16.8 Functions with array parameters
16.9 Functions with array parameters: Common errors
16.10 Engineering examples using functions
16.11 Grouping data: struct
16.12 Structs and functions
16.13 Structs and vectors
16.14 Structs, vectors, and functions: A seat reservation example
16.15 Command-line arguments
16.16 Command-line arguments and files
16.17 The #define directive
16.18 Modular compilation
16.19 Makefiles
16.20 Additional practice: Output art
16.21 Additional practice: Grade calculation
16.22 Additional practice: Tweet decoder
16.23 Additional practice: Dice statistics
16.24 zyBooks built-in programming window
Teach C++ with this hands-on, interactive zyBook, now updated with Advanced zyLabs
Programming in C++ is a comprehensive introduction to the principles and practice of C++ programming, based on the latest standards.
- Covers foundational constructs, like branches, loops and functions, and advanced topics, like inheritance, exceptions and plotting
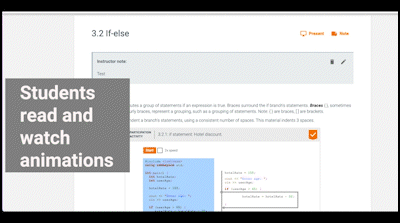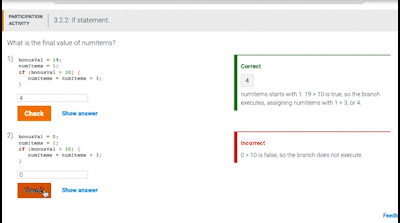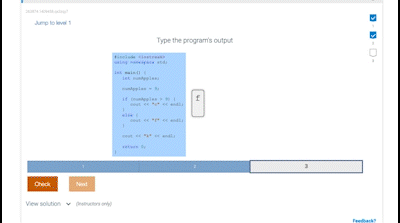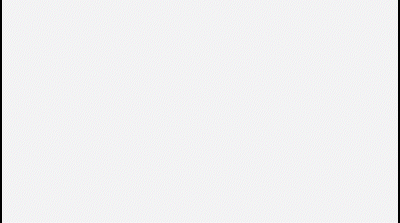
- Packed with over 700 interactive coding exercises and learning activities to help students master the material
- Includes emphasis on disciplined program development, incremental development, modular development, and testing/debugging.
- Completely customizable so instructors can reorganize, edit and add their own learning content
- Adopters have access to a test bank with questions for every chapter
What is a zyBook?
Programming in C++is a web-native, interactive zyBook that helps students visualize concepts to learn faster and more effectively than with a traditional textbook. (Check out our research.)
Since 2012, over 1,700 academic institutions have adopted digital zyBooks to transform their STEM education.
Our Programming C++ zyBook provides students with an interactive and engaging learning environment with a solid understanding of memory. From the moment variables are introduced, the material shows via animations how variables exist and are updated in memory. The continued showing of memory throughout helps clarify challenging topics like pass-by-copy/reference parameters, vectors/arrays, pointers, and more.
The zyBooks Programming Environment
See the new Advanced zyLabs capabilities:
Authors
Frank Vahid
Professor of Computer Science and Engineering, Univ. of California, Riverside
Roman Lysecky
Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Univ. of Arizona